
Special raw materials and stainless steels
for high-quality connecting elements
We are a leading specialist for high-quality connecting elements made of various special materials and stainless steels. You will find materials with different properties in our assortment.
Our selection ranges from conventional A2 screws to connecting elements including threaded rods, washers and nuts made of materials that are highly resistant to corrosion. We currently
have one of the largest warehouses for threaded rods in 1.4529, 1.4462 and 1.4571. We are more than happy to cut threaded bolts according to the requirements of our customers.
We offer the right stainless steel screws for every application.
Due to the new actualization of standards of ISO 3506-6:2020, the materials of CRC IV and CRC V on our stock are now also classified into the new steel grades A8, D8 and D6.
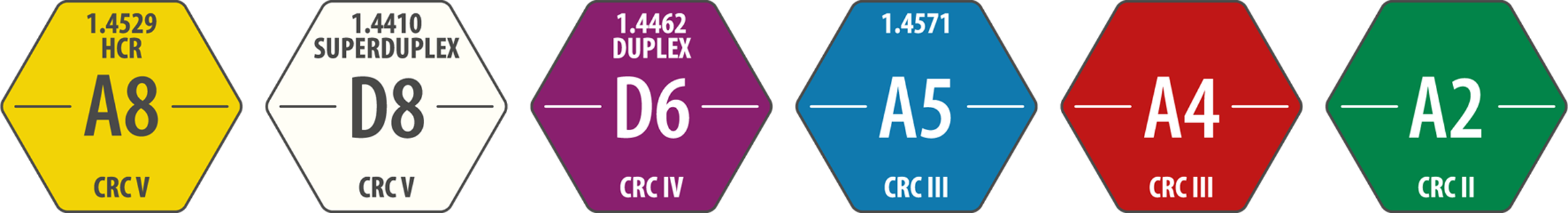
Conventional special materials always in stock
Conventional and frequently requested special materials, such as A8 (1.4529 HCR), D6 (1.4462 DUPLEX) and A5 (1.4571) as well as A4 and A2 stainless steels are immediately available from our warehouse. The “king” amongst our special materials is Alloy 926 (material 1.4529), which is extremely resistant to corrosion, more so than the other non-corroding austenitic stainless steel materials available. Only one step behind is the 1.4462 duplex steel. It has a very high strength and is classified in corrosion resistance class CRC IV. The third highest grade of special material in stainless steel is material 1.4571 together with 1.4401 and 1.4404. This means that the right material for each of the five corrosion resistance classes (CRC) is directly available to you from our warehouse. If you require stainless steel with good acid and corrosion resistance according to Class III, then our titanium-stabilized material 1.4571 (A5) and 1.4401 and 1.4404 (A4) stainless steels offer perfect solutions. It is no coincidence that screws in A4 stainless steel can be found in many areas of connection technology. The most commonly used stainless steel is A2 stainless steel, which is also known as AISI 304. About one third of stainless steel production can be assigned to this type of alloy. A2 screws comply with corrosion resistance class II. Typical applications for A2 screws are wood fittings, device assembly or kitchen appliances.
Lots of other special materials with special properties
In addition to the standard special materials and screws made of A2, A4, 1.4571, 1.4462 DUPLEX and 1.4529 HCR, we also supply lots of other special materials for special applications on request. Although you will not find them in our product catalogue, we will be more than happy to procure them on your behalf on a project-by-project basis. Our other special materials are divided into the following three groups:
- Heat-resistant special materials
- Super-duplex special materials
- High-alloy special materials
Important alloying elements and microelements in stainless steels
What do the chemical elements molybdenum, sulphur, aluminium, chrome, niobium, carbon, silicon, copper, manganese, nickel, nitrogen, titanium, and vanadium have in common? They all are alloying elements and microelements of stainless steel.
But which effect does every single element have towards stainless steel and in which composition? Does the material become harder or more resistant against corrosion? Which influence do the elements have on the characteristics of the material? What does the effective sum W (or in English: PREN) declare and how is it determined?
You can find a compact summary about this topic here: Important alloying elements and microelements in stainless steels.
Choice of material according to corrosion resistance classes
Corrosion resistance classes (CRC) are of central importance for the selection of suitable materials. They can be divided into five different classes, depending on the basic elements used for the materials and the composition of the alloys. The classes determine the extent to which the connecting elements made of the materials fulfil the expectations for corrosion resistance in buildings. Architects, construction planners and engineers need to comply with the resistance classes when selecting and procuring the connecting elements. The material specified by the standard always needs to be selected depending on whether a stainless steel screw is used in an indoor pool, close to the sea or in a dry environment. Safety is of the highest priority here!
If you have any questions on this topic, do not hesitate to contact our expert staff by phone, web form or email.
They will be more than happy to provide you with detailed advice and find the right material for you.

Our Sales Team will be more than happy to help you further:
T: +49 7941 6073-0 sales@tobsteel.com
